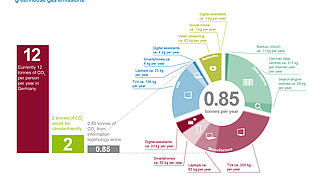
Digital technologies and business models have become a ubiquitous feature of our lives – at home and in the workplace. Computers, smartphones, digital mobile services and cloud computing all form part of the ongoing digital transformation of our economy and society. However, new social and economic problems are becoming apparent at the same time. When it comes to environmental protection and sustainability, the impacts of this transformation are far-reaching – and ambiguous. Digital technologies can make a direct contribution to energy and resource efficiency. But they can also have the opposite – negative – effect if the manufacture and use of digital devices lead to increased consumption of energy and materials.
“Thinking big” about digitalisation, climate change mitigation and justice; embedding sustainability as a key benchmark in digitalisation processes; defining innovation targets for energy and resource efficiency – from the Oeko-Institut’s perspective, these are core fields of action in a sustainable approach to digitalisation. Policy-makers and business have a key role to play by setting frameworks and delivering on objectives. The Oeko-Institut shares its knowledge and makes practical recommendations on how to build sustainability into the digital transformation.


![[Translate to English:] © plainpicture/Mint Images](/fileadmin/_processed_/3/f/csm_Digitalisierung-Digitale-Infrastruktur_plainpicture-Mint-Images_69482954c2.jpg)

![[Translate to English:] © plainpicture / Vitta Gallery](/fileadmin/_processed_/3/5/csm_Digitalisierung-IT-Anwendungen_plainpicture-Vitta-Gallery_f54b00126f.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] © plainpicture / Maskot](/fileadmin/_processed_/f/f/csm_Digitalisierung-KI-Software_plainpicture-Maskot_edc482f265.jpg)